<- Back to the Teaching of Morimoto Lab
Processing01
In this class, we do programming using
- image, 3d model, interaction, sound, motion, device(camera etc).
- Processing01
- Tool: Install it before the class!
- What Processing can do
- Schedule of this lecture
- Install Processing ver 3 (for Win)
- Basic drawing
- Display text
- Basic programming
- Ex5: Define & calculate using the data types and write these processes to console.
- Ex6: Try to use “String” data with “+” operator.
- Ex7: Display numbers from 0 to more than 10 in black color using “for”.
- Ex8: (Using the code of the above Ex,) Change colors of numbers if they are multiples of 3.
- Ex9: Try to use “if” with boolean data without any operators.
- Image
- Structuring
- Animation
- move
- rotate
- Ex17: Try this code & remember the circle equation.
- Ex18: Change the line length to 222 pix in following way.
- Ex19: Do Ex18 by using “dist(), div(), mult()” of PVector.
- Ex20: Rotate circle around a center point of the window.
- Ex21: Rotate line around a center point of the window.
- (Ex22: Can you make clock-like behavior?)
- Affine transform
- Affine methods of Processing
- Interaction
- Save, Export image & animation
- Points
- Reference web
- Homework: Complete the exercises as possible.
- Contact
Tool: Install it before the class!
Processingis used for this class!
- Might not be unsuitable for big/ complicated program.
- OpenFrameworks, Unity, Maya (mel)
- would be ok but are not supported in this class.
What Processing can do
Debug
Text
Mouse & keyboard
Arrays
Transformations
Math, trigonometry
Image (SVG, OpenCV, )
Video
Sound
Motion
3D model
Object
Curve
GUI
Electronics
Network
Web (p5.js, applet?)
Android
(This article)
(Another day)
(Do not support in this class?)
See official Processing tutorials on web.
See sample codes (file > samples)
Schedule of this lecture
| 0 | Orientation |
|---|---|
| 1-2 | Basis of programming, math, physics |
| 3-4 | Computer vision (OpenCV), video |
| 5-6 | Sound & interaction |
| 7-8 | Motion & model & texture mapping |
| 9-10 | What & how to make? Workshop & presentation. |
| 11-12 | Time to implement. Plan exhibition. |
| 13-14 | Exhibition. |
Install Processing ver 3 (for Win)
- Download Processing [official Processing web]
- Unzip
- Place at “C”
- Make shortcut
- From setting, confirm that the place of sketchbook (.pde file) is C:\Users\yuki(user name)\Documents\Processing
- From setting, select “Language > Japanese” if you need

Launch Processing > File > Sample > Demo > Particle

First programming.
Launch Processing -> Write like this -> Push execution button (or Ctrl+r).
size(200,200);//window size.
point(10,10);//draw point at this position.
If a window like the below appears, it is ok.
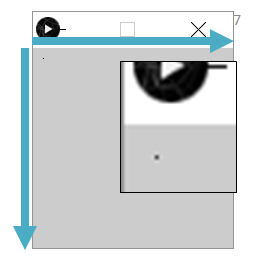
Coordinate system: Upper left is origin, vertically opposite.
Basic drawing
- size(windowWidth, windowHeight)
- point(positionX, positionY)
- line(startPosition X, Y, endPosition X, Y)
- ellipse(centerPosX, Y, width, height)
- rect(pos X, pos Y, width, height)
- colorMode(“HSB” or “RGB”)
- background(H,S,B) or (R, G, B) or (#HTML hex num)
- See: Tool > Color selector
- Try: background(gray);
- fill(color, opacity)
- noFill()
- stroke(color)
- noStroke()
[official tutorial for coordinate system and shapes, color, ]
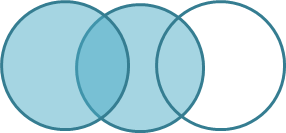
Ex1: Make an image like upper one.
(Ex2: Create a person using Processing. )
Display text
- textSize(text size);
- text(“characters”, position X, position Y);
#How to specify font type? See below.
PFont aaa= createFont("Calisto MT Bold Italic",20);
textFont(aaa);
fill(15,140,240);
text("HelloWorld",50,100);
//Try: println(PFont.list());
Ex3: Display “HelloWorld” on screen.
Ex4: Use some other font.
Basic programming
| Data type | Operator | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| int | integer number | + | add | |
| float | decimal | - | subtract | |
| color | such as RGB, HSB, | * | multiply | |
| char | one character/letter | / | divide | |
| String | many characters | % | modulo | |
| Boolean | ”true” or “false” | ++ | inclement | |
| – | declement |
Useful methods
- println(data/character) : write characters in a line into the console.
- random(lower limit, upper limit) : generate random number between specified range.
Ex5: Define & calculate using the data types and write these processes to console.
- !Do not transform to other data type!
Ex6: Try to use “String” data with “+” operator.
| Operator to compare | |
|---|---|
| < | |
| > | |
| <= | |
| = | |
| != | |
| == | Note: “==” is not “=”. |
Repetition
- for
- while
- continue
- break
[ official reference for for loop, while, continue, break, ]
Condition
- if
- else
[ official reference for if, else, ]
Ex7: Display numbers from 0 to more than 10 in black color using “for”.
Ex8: (Using the code of the above Ex,) Change colors of numbers if they are multiples of 3.
Ex9: Try to use “if” with boolean data without any operators.
Image
PImage img = loadImage("sura.png");
image(img, 100, 100, img.width/4, img.height/4);
- Pimage : data type for image.
- loadImage(“file name”) : load image file.
- put image file in the same folder with ".pde" (sketchbook).
- use relative pass if the file is placed in the other folder.
- Image(PImage, pos X, pos Y, width, height) : display PImage data.
Structuring
Structure your Processing code by 3 parts .
//Before structuring
int a;
a=0;
a++;
println(a);//a is 1
//After structuring
//★1. usually define global data (variables).
int a;
//★2. only once at first time
void setup()
{
size(300,300); //size() must be here.
a=0;
}
//★3. repeated after setup
void draw()
{
a++;
println(a);//a is 1,2,3,4,5,…
}
Point:
You have to decide where each step should be.
Lower computational cost is preferred.
Scope
Scope : Defined data can be used in
the smallest enclosed area.This area is scope.
Global variables : Defined data in other than enclosed area. It can be usedeverywhere in this program.
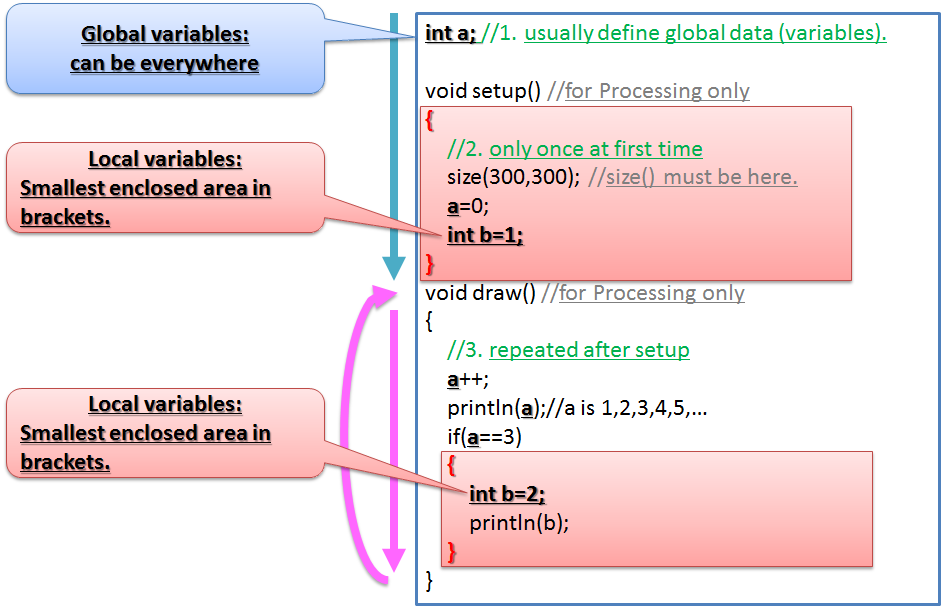
Original method
You can define original method such as the below.
//1. usually define global data (variables).
int a;
void setup()//2. only once at first time
{
size(300,300); //size() must be here.
a=0;
}
void draw() //3. repeated after setup
{
myFuncVoid();
myFuncInt();
float aaa = myFuncFloat(5.0);
}
void myFuncVoid()//void: no return
{
println(“Hello!”);
}
int myFuncInt()//int: return int
{
int a = 0;
return a;
}
float myFuncFloat(float a)//float: return float
{
return a + 1.5f;
}
Note: Method’s parameters can be multiple such as below.
float myFuncFloat(int a, float b, color c, PImage img)
Ex10: Try this code & change the methods.
Ex11: (Advanced ex) Search & use “class”.
Animation
move
How to animate a ball?
int px=100;
int py=100;
void setup()
{
size(500, 500);
}
void draw()
{
//hint 2: paint background
ellipse(px,py,100,100);
//hint 1: change px/py values using px/py
}
Ex12: Animate an ellipse from left to right.
Point:
Draw() repeats its contents.
px & py are changed in draw() using themselves before.
So, px & py should be global data.
Ex13: Animate an ellipse from left to right by velocity values.
int px=100;
int py=100;
int vx = 1;//velocity x
int vy = 1;//velocity y
...
Ex14: Bounce it like below.
Ex15: Consider gravity, air drag, reflection coefficient, etc.
...
int vy = 1;//velocity y
final float GRAVITY = .9f;
final float AIR_DRAG = 0.99f;
final float WALL_DRAG = 0.99f;
final float REFLECTION_COE = 0.9f;
...
Ex16: Replace px,py,vx,vy by using “PVector”.
//How to use PVector
PVector pos=new PVector(100, 100);//define & initialize
ellipse(pos.x, pos.y, 100, 100);
rotate
Ex17: Try this code & remember the circle equation.
float ballSize = 100;
PVector pos;// = new PVector();//(0,0)
float deg = 0;
float r = 300;
void setup()
{
size(500,500);
}
void draw()
{
background(255);
ellipse(pos.x, pos.y, ballSize, ballSize);
pos.x = r * cos(radians(deg));
pos.y = r * sin(radians(deg));
deg++;//same with deg=deg+1;
//if(deg>360)deg=0;
PVector tem = new PVector(pos.x, pos.y);
line(0,0,tem.x, tem.y);
}
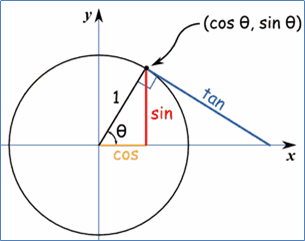
Remember the equation of circle centered at the origin.
Ex18: Change the line length to 222 pix in following way.
- Calculate the distance between origin and tem by sqrt().
- Divide tem.x,y by the distance.
- Multiply 222 to tem.x, y.
Ex19: Do Ex18 by using “dist(), div(), mult()” of PVector.
float di = tem.dist(new PVector(0,0));
float di = PVector.dist(tem, new PVector(0,0));
tem.div(di);//is same with "tem = PVector.div(tem, di);"
Then, you can use “normalize()” of PVector!
tem.normalize();//tem is normalized.
Ex20: Rotate circle around a center point of the window.
You can use witdh, height as window size.
Ex21: Rotate line around a center point of the window.
You have to move the start & end points.
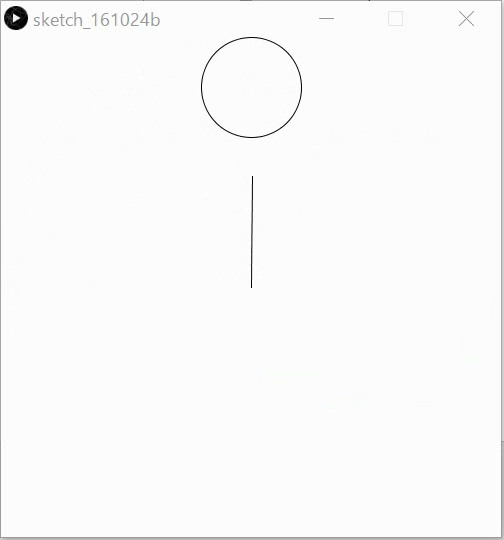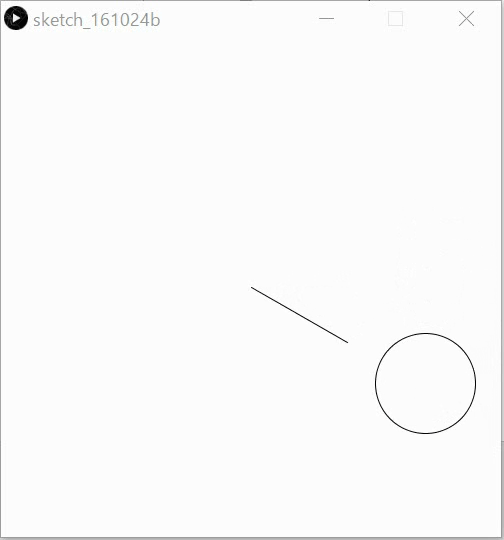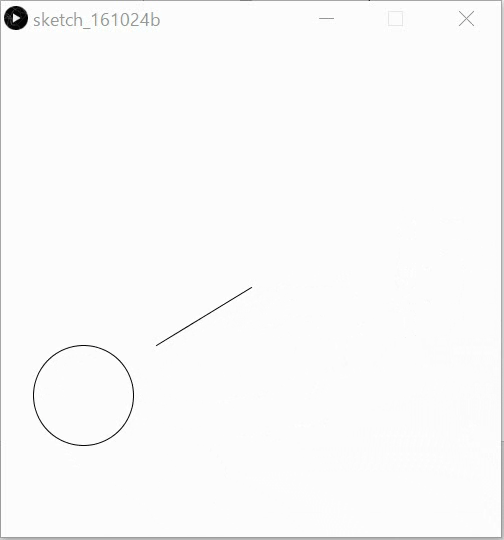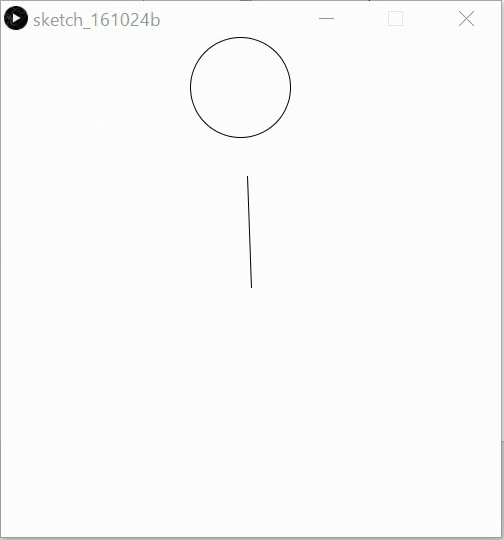
(Ex22: Can you make clock-like behavior?)
Affine transform
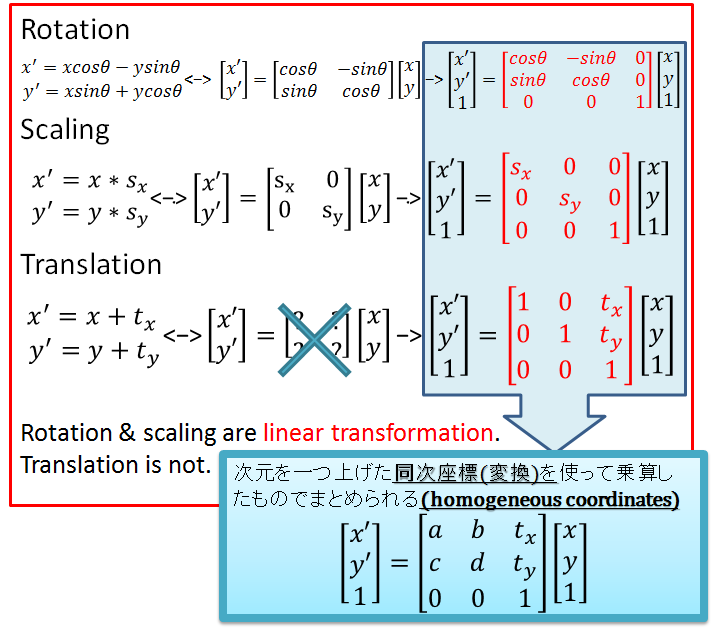
[同次座標変換]
Affine methods of Processing
- rotate(radian)
- translate(x move, y move)
- scale(x scale, y scale)
- pushMatrix() & popMatrix()
//sample code of affine methods
float ballSize = 100;
PVector pos = new PVector(0, 0);
float deg = 0;
float r = 100;
void setup(){
size(500, 500);
}
void draw()
{
background(255);
rotate(radians(deg));
translate(r,0);
//scale(1.3);//same with scale(1.3, 1.3);
ellipse(pos.x, pos.y, ballSize, ballSize);
deg++;
}
//sample code of push and popMatrix.
pushMatrix();
translate(100, 0);
ellipse(pos.x, pos.y, ballSize, ballSize);
//popMatrix();
//pushMatrix();
translate(300, 0);
ellipse(pos.x, pos.y, ballSize, ballSize);
popMatrix();
Ex23: Try to use methods of affine transform.
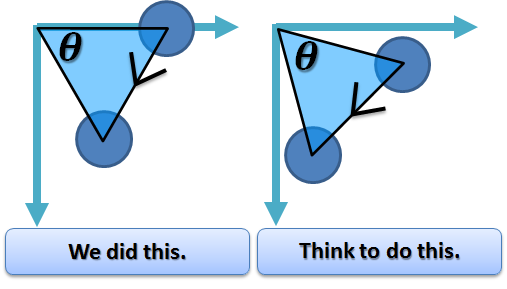
Note: The order of affine methods is opposite! However, the methods of such as ellipse(), image(), and so on should be below of these affine methods.
Ex24: Implement the below behaviors by affine methods.
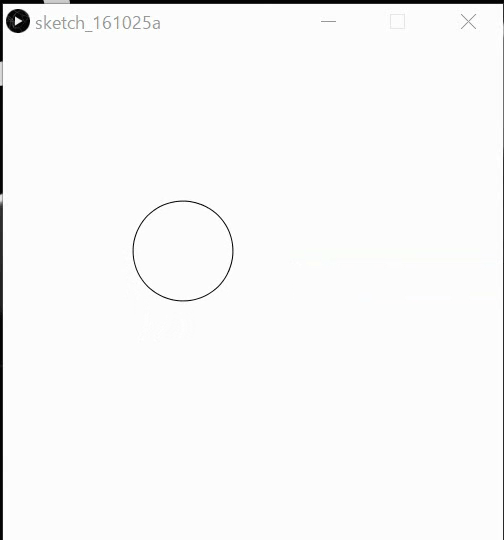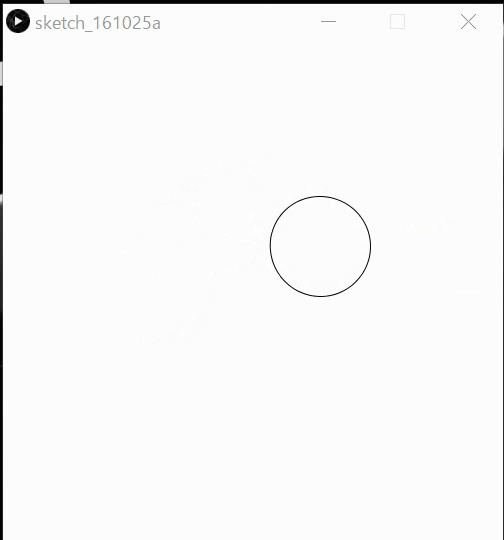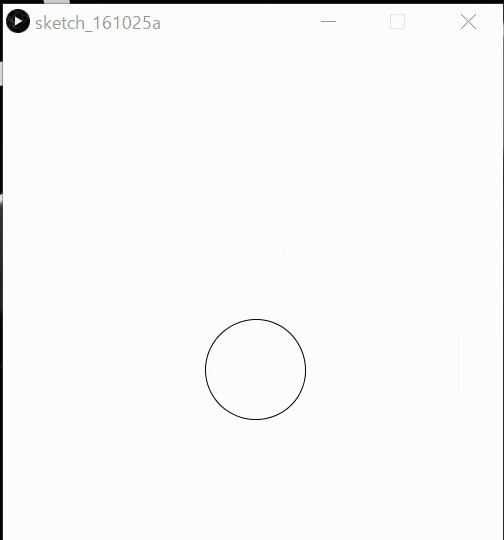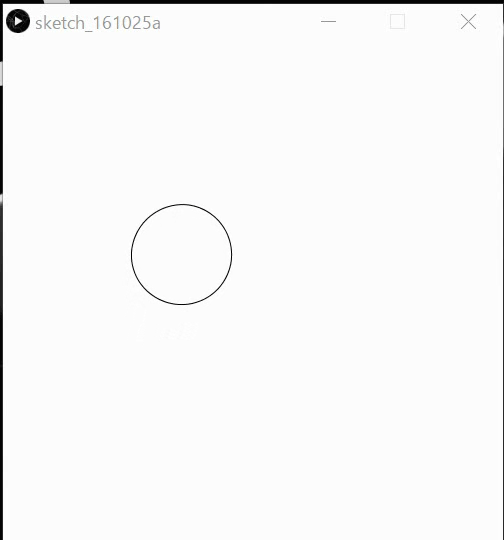
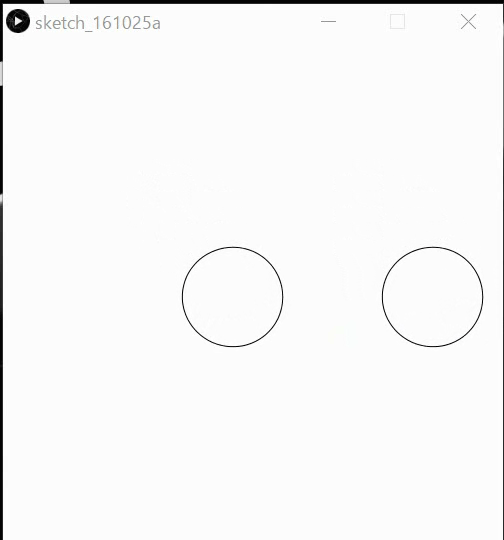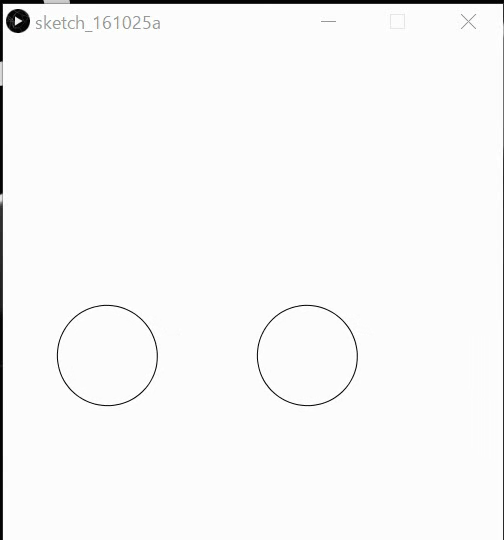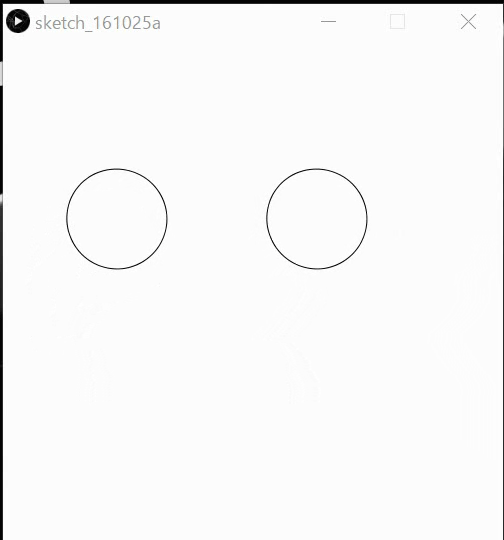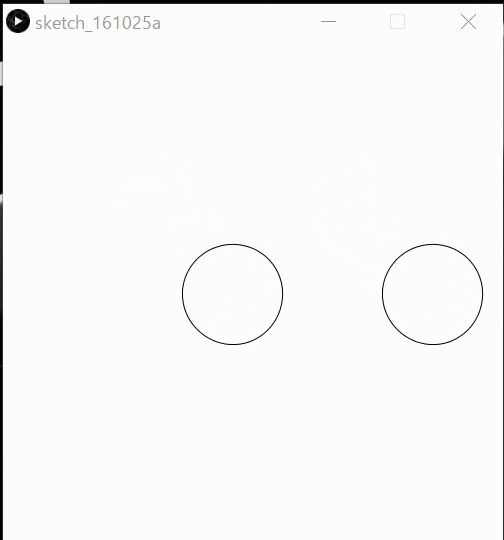
Interaction
Mouse & Keyboard
- mouseX, mouseY :mouse position (int)
- pmouseX, pmouseY :previous mouse position (int)
- mousePressed, etc : see sample 1.
keyPressed, etc : see sample 2.
sample 1 : Output->
void mousePressed() {//mouseReleased()
if ( mouseButton == LEFT ) {
println("m left");
}
else if ( mouseButton == CENTER ) {
println("m center");
}
else if ( mouseButton == RIGHT ) {
println("m right");
}
}sample 2 : Output->
int cou=0;
void setup(){
size(500, 500);
PFont font = createFont("Naiv-Fat", 42);
textFont(font, 24);
background(255);
}
void keyPressed() {
if (key=='3') fill(255, 0, 0);
else fill(100, 100, 255);
text(key, 100+cou*20, 100);
cou++;
}
void draw(){}
Ex25: Implement like this by mouse interaction.

Ex26: Implement like this by keyboard interaction.

Save, Export image & animation
- save(“filename.xxx”)
- capture the screen & save it as an image file.
- saveFrame(“####.xxx”)
- save sequentially numbered image files.
- Tool > movie maker
- Indicate folder of sequential images.
- File > Export as an application
- Select win/mac/linux and push “export”.
- Create “data” folder in the same level with .pde to put media files.
- Click .exe in the “application.xxx” folder.
Ex27: Save image & movie.
sample code.
float ballSize = 100, deg = 0, r = 80;
PVector pos = new PVector(0, 0);
void setup(){
size(500, 500);
background(255);//can be in draw()
}
void draw(){
translate(width/2, height/2);
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {//any animation
rotate(radians(deg));
translate(r, 0);
ellipse(pos.x, pos.y, ballSize, ballSize);
}
deg++;
saveFrame("frames/####.tif");
//#: digit number, tif: recommended,
//frames: foldername (then, a folder is created)
}
void keyPressed(){
if ( key == ' ' ) save( "hoge.png" );
}
Ex28: Export .exe.
Points
Comprehensible program
- Empty line, {}, indent (tab button, Ctrl+T), comment (//, /**/)
- Comprehensible name of variables & original methods
Search by yourself
- Ex can’t be solved by the information of this material sometimes.
- If you cannot get the answer by yourself , then ask skilled person!
Reference web
- Processing
- Reference
- On web, or,
- Right click on a method of code >
find from reference(win) - Must see
Math, Constants, Shape (2D), etc, because the contents in this site were not all for each category.
- Others
- Official information on the left menu
- Reference
- Processing入門講座
- Mainly refer here for this slide
- Processing学習ノート [draw figures]